MOST COMMON
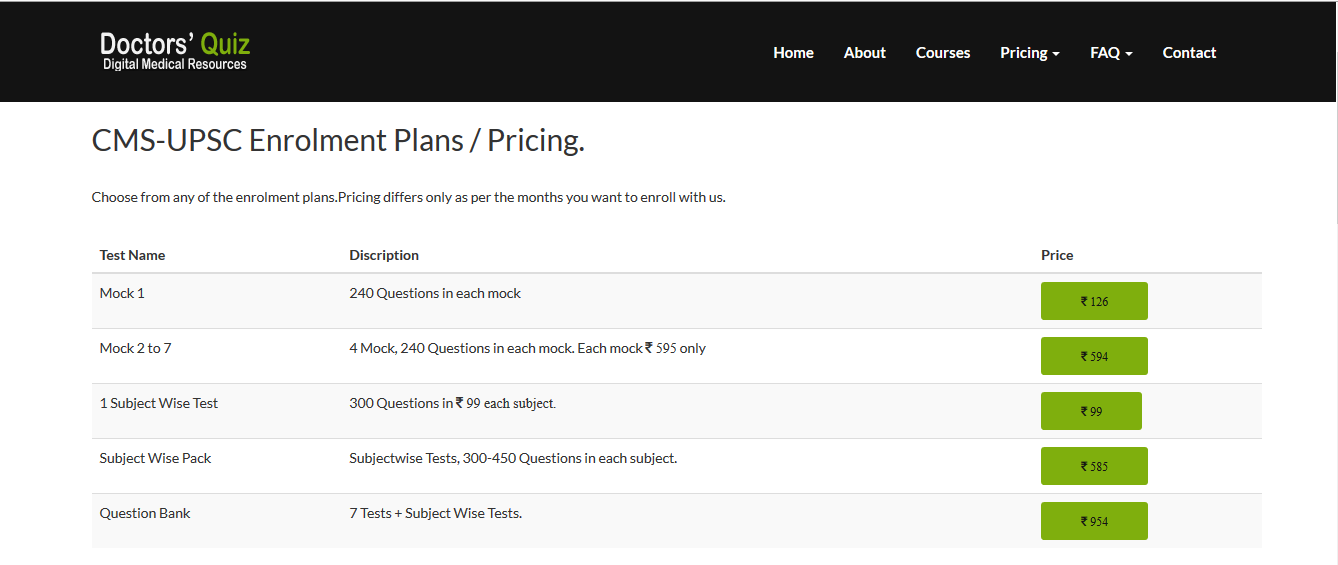
| 1° Tumor arising from bone in adults | Multiple Myeloma |
| Adrenal Medullary Tumor Adults | Pheochromocytoma |
| Adrenal Medullary Tumor Children | Neuroblastoma |
| Bacterial Meningitis adults | Neisseria meningitidis |
| Bacterial Meningitis elderly | Strep pneumoniae |
| Bacterial Meningitis newborns | E. coli |
| Bacterial Meningitis toddlers | Hib |
| Bone Tumors | Metasteses from Breast & Prostate |
| Brain Tumor Child | Medulloblastoma (cerebellum) |
| Brain Tumor Adult | Astrocytoma (including Glioblastoma Multiforme) then: mets, meningioma, Schwannoma |
| Breast Carcinoma | Invasive Duct Carcinoma |
| Breast Mass | Fibrocystic Change (Carcinoma is the most common is post-menopausal women) |
| Bug in Acute Endocarditis | Staph aureus |
| Bug in debilitated, hospitalized pneumonia pt | Klebsiella |
| Bug in Epiglottitis | Hib |
| Bug in GI Tract | Bacteroides (2nd E. coli) |
| Bug in IV drug user bacteremia / pneumonia | Staph aureus |
| Bug in PID | N. Gonnorrhoeae |
| Bug in Subacute Endocarditis | Strep Viridans |
| Cardiac 1° Tumor Adults | Myxoma "Ball Valve" |
| Cardiac 1° Tumor Child | Rhabdomyoma |
| Cardiac Tumor Adults | Metasteses |
| Cardiomyopathy | Dilated (Congestive) Cardiomyopathy |
| Cause of 2° HTN | Renal Disease |
| Cause of Addison's | Autoimmune (2nd infection) |
| Cause of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia | 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency (then, 11-) |
| Cause of Cushings | Exogenous Steroid Therapy (then, 1° - ACTH, Adrenal Adenoma, Ectopic ACTH) |
| Cause of death in Alzheimer pts | Pneumonia |
| Cause of death in Diabetics | MI |
| Cause of Death in SLE pts. | Lupus Nephropathy Type IV (Diffuse Proliferative) |
| Cause of Dementia | Alzheimer's |
| Cause of Dementia (2nd most common) | Multi-Infarct Dementia |
| Cause of food poisoning | Staph aureus |
| Cause of mental retardation | Down's |
| Cause of mental retardation (2nd most common) | Fragile X |
| Cause of preventable blindness | Chlamydia |
| Cause of Pulmonary HTN | COPD |
| Cause of SIADH | Small Cell Carcinoma of the Lung |
| Chromosomal disorder | Down's |
| Congenital cardiac anomaly | VSD (membranous > muscular) |
| Congenital early cyanosis | Tetralogy of Fallot |
| Coronary Artery thrombosis | LAD |
| Demyelinating Disease | Multiple Sclerosis |
| Dietary Deficiency | Iron |
| Disseminated opportunistic infection in AIDS | CMV (Pneumocystis carinii is most common overall) |
| Esophageal cancer | SCCA |
| Fatal genetic defect in Caucasians | Cystic Fibrosis |
| Female Tumor | Leimyoma |
| Form of Amyloidosis | Immunologic (Bence Jones protein in multiple myeloma is also called the Amyloid Light Chain) |
| Form of Tularemia | Ulceroglandular |
| Gynecologic malignancy | Endometrial Carcinoma |
| Heart Murmur | Mitral Valve Prolapse |
| Heart Valve in bacterial endocarditis | Mitral |
| Heart Valve in bacterial endocarditis in IV drug users | Tricuspid |
| Heart Valve involved in Rheumatic Fever | Mitral then Aortic |
| Hereditary Bleeding Disorder | Von Willebrand's Disease |
| Liver 1° Tumor | Hepatoma |
| Liver Disease | Alcoholic Liver Disease |
| Location of Adult brain tumors | Above Tentorium |
| Location of Childhood brain tumors | Below Tentorium |
| Lysosomal Storage Disease | Gaucher's |
| Motor Neuron Disease | ALS |
| Neoplasm Child | Leukemia |
| Neoplasm Child (2nd most common) | Medulloblastoma of brain (cerebellum) |
| Nephrotic Syndrome | Membranous Glomerulonephritis |
| Opportunistic infection in AIDS | PCP |
| Ovarian Malignancy | Serous Cystadenoma |
| Ovarian Tumor | Hamartoma |
| Pancreatic Tumor | Adeno (usually in the head) |
| Patient with ALL / CLL / AML / CML | ALL - Child / CLL - Adult over 60 / AML - Adult over 60 / CML - Adult 35-50 |
| Patient with Goodpasture's | Young male |
| Patient with Reiter's | Male |
| Pituitary Tumor | Prolactinoma (2nd Somatotropic "Acidophilic" Adenoma) |
| Primary Hyperparathyroidism | Adenomas (followed by: hyperplasia, then carcinoma) |
| Pt. With Hodgkin's | Young Male (except Nodular Sclerosis type Female) |
| Pt. With Minimal Change Disease | Young Child |
| Secondary Hyperparathyroidism | Hypocalcemia of Chronic Renal Failure |
| Sexually transmitted disease | Chlamydia |
| Site of Diverticula | Sigmoid Colon |
| Site of metastasis | Regional Lymph Nodes |
| Site of metastasis (2nd most common) | Liver |
| Sites of atherosclerosis | Abdominal aorta > coronary > popliteal > carotid |
| Skin Cancer | Basal Cell Carcinoma |
| Stomach cancer | Adeno |
| Testicular Tumor | Seminoma |
| Thyroid Cancer | Papillary Carcinoma |
| Tracheoesophageal Fistula | Lower esophagus joins trachea / upper esophagus blind pouch |
| Tumor of Infancy | Hemangioma |
| Type of Hodkin's | Mixed Cellularity (versus: lymphocytic predominance, lymphocytic depletion, nodular sclerosis) |
| Type of Non-Hodgkin's | Follicular, small cleaved |
| Vasculitis (of medium & small arteries) | Temporal Arteritis |
| Viral Encephalitis | HSV |
| Worm infection in US | Pinworm (2nd Ascaris) |